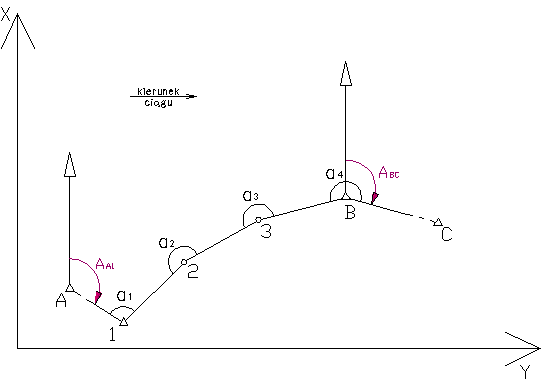
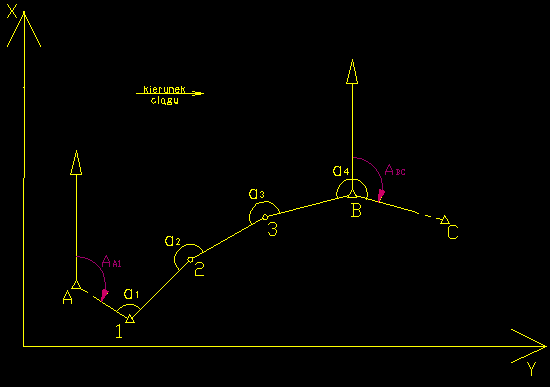
Calculating the traverse tied up at both ends
***Completion of a closed traverse
Traverse is a geometric design used to determine the coordinates of the points during which the sides and angles measured.
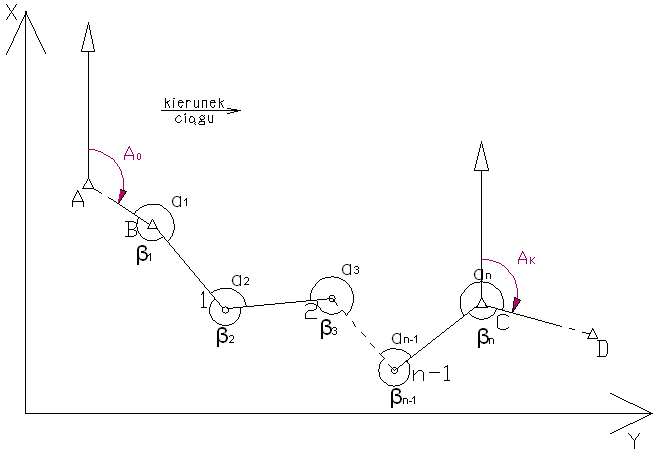
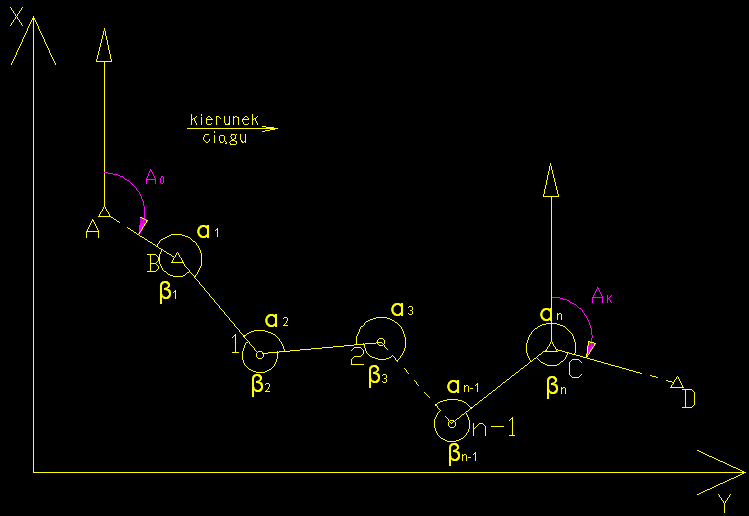
Figure 1. the traverse tied up at both ends
Search:
1 (X1, Y1)
2 (X2, Y2)
3 (X3, Y3)
Data:
A (XA, YA)
B (XB, YB)
C (XC, YC)
D (XD, YD)
Measured
- left angles: α1, α2, α3, ..., αn
or
- right angles: β1, β2, β3, ..., βn
- length: d12, d23, ..., dn-1 - n
1. First, from coordinates of the geodetic connection points we determine an initial bearing* A0 a final bearing * Ak in the traverse.
*If you do not remember how to calculate the bearing from coordinates of two points, click 
2. Calculate the practical sum of the angles ∑αp (or ∑βp),which is the sum of the measured angles and the theoretical sum:
∑αt = Ak – A0 + n•200g,0000 in the case of the angles of the left
∑βt = A0 – Ak + n•200g,0000 in the case of the angles of the right
where n – number of angles in the traverse.
***In the closed traverse:
- for interior angles: ∑αt = (n-2)•200g,0000
- for external angles: ∑βt = (n+2)•200g,0000
3. On the basis of practical and theoretical sum of the angles we calculate the angular deviation:
fα = ∑αp – ∑αt ,
fβ = ∑βp – ∑βt
Check to see if it satisfies the condition f ≤ fdop, where
fdop= m0√_
nk. Exemplary values fdop
are tabulated in the Technical Manual, G-4, zał.2. In 30% of cases are allowed to double the value of fdop.
4. After evaluating the correctness of the above condition, we proceed to calculate the corrections for different angles:
vαi = – fα
n
vβi = – fβ
n
The sum of the angular corrections must be equal to the angular deviation in absolute value.
5. Then compensates for the measured angles:
_
αi = αi + vαi
_
βi = βi + vβi
6. Starting from the initial bearing A0 we calculated compensated bearings for each additional side:
Ai = Ai-1 +
_
αi – 200g,0000
Ai = Ai-1 –
_
βi + 200g,0000
Compensated bearing for the last side should be equal to the final bearing Ak.
7. Having compensated bearings Ai calculate the northing and the easting difference:
Δxi = dicosAi
Δyi = disinAi
8. Received the northing and the easting differences add up, so we get a practical sum of the northing and the easting differences ∑Δxp, ∑Δyp.
The theoretical sum of the northing and the easting differences is calculated of the coordinates of starting and ending point in the traverse:
∑ΔXt = XC – XB
∑ΔYt = YC – YB
***In the closed traverse: ∑ΔXt= 0 oraz ∑ΔYt= 0.
9. We define the deviation for the northing and the easting differences:
fx = ∑ΔXp – ∑ΔXt
fy = ∑ΔYp – ∑ΔYt
and the linear deviation:
fL = √_________
fx2 + fy2
Check the condition fL ≤ fLdop,
where
fLdop
=√_____________________________
u2L+(m0/ρ)2(n+1)(n+2)(L2/12n)+c2
Exemplary values fLdop
are tabulated in the Technical Manual, G-4, zał.3.
***In the closed traverse: fx= ∑ΔXp oraz fy= ∑ΔYp.
10. Adding correction for each the northing and the easting difference, which is expressed by the formula:
vxi = – fx di
d
vyi = – fy di
d
Check: Σvxi = – fx , Σvyi= – fy.
We get compensated for the northing and the easting differences:
__
ΔXi = Δxi + vxi
__
ΔYi = Δyi + vyi
11. Calculate the compensated coordinates of the searched points:
_
Xi = Xi-1 + __
ΔXi
_
Yi = Yi-1 + __
ΔYi
12. We check the calculations:
_
Xn = Xn-1 + __
ΔXn = Xn
_
Yn = Yn-1 + __
ΔYn = Yn
|
 Search
Search